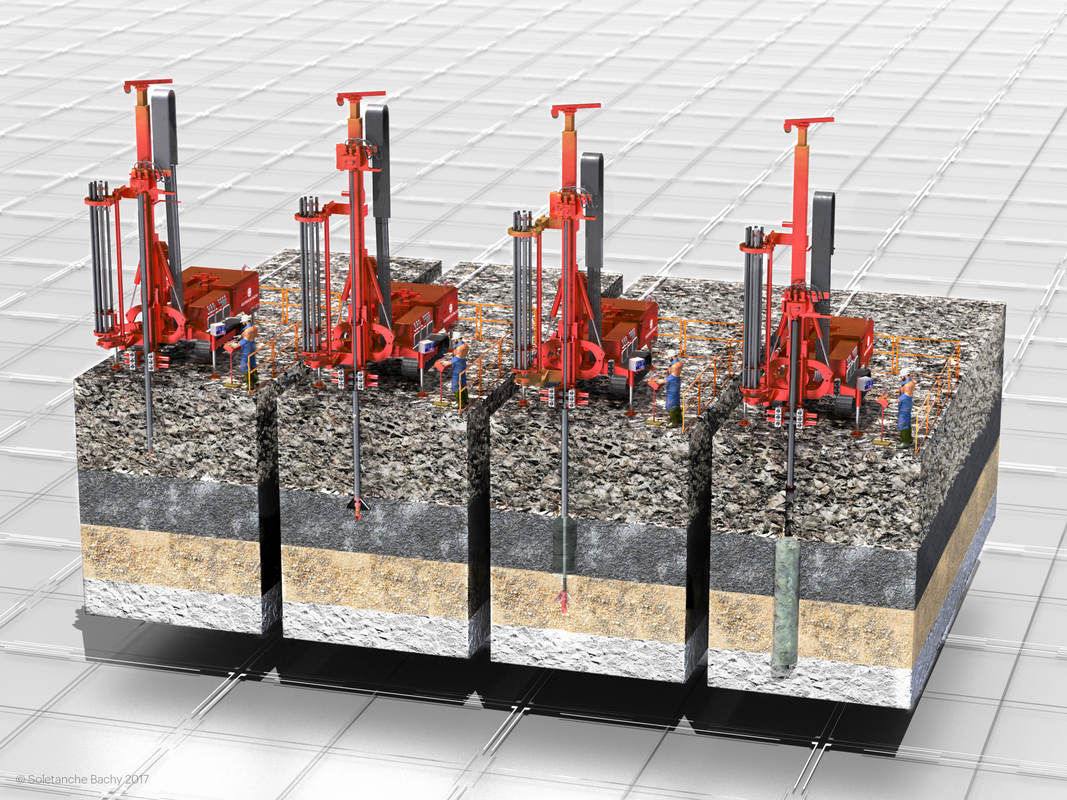
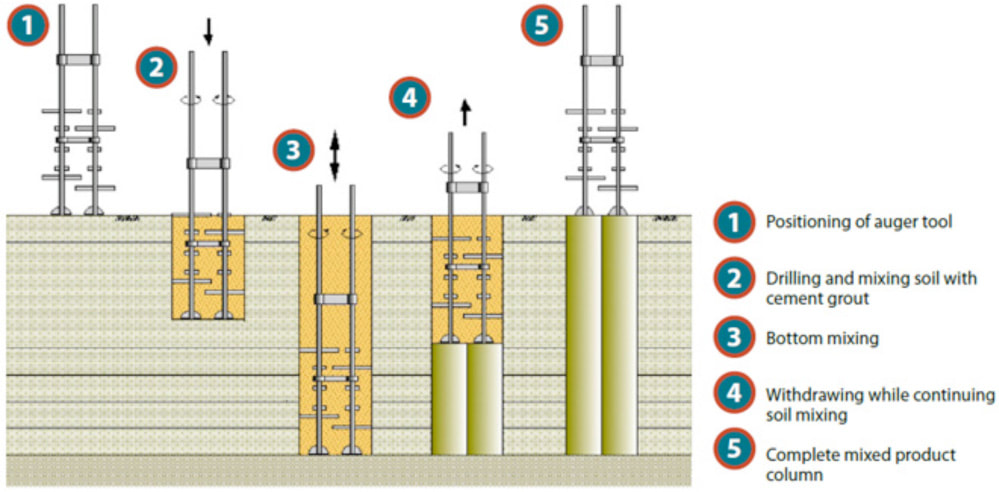
cement- based soil mixing
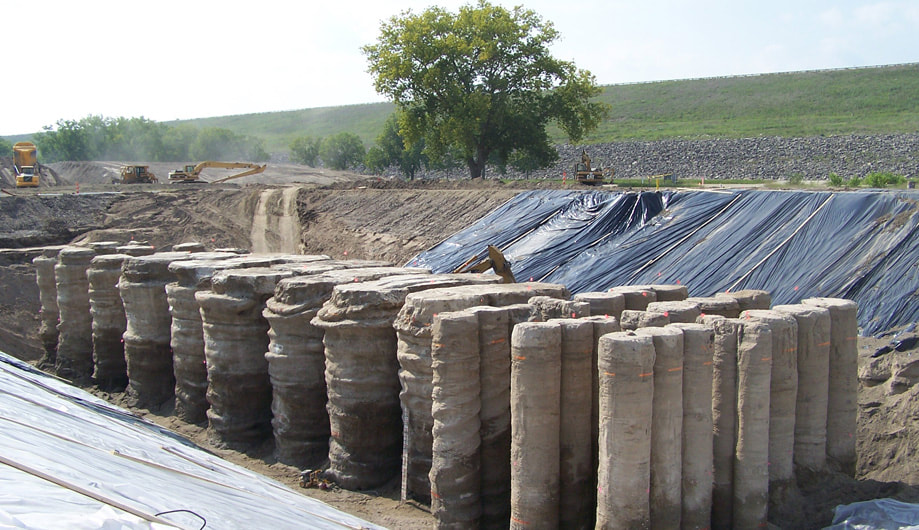
The stabilization technology by Deep Soil Mixing is based on introducing and mixing additives (stabilizing agents) into the ground, as powder or as a suspension, using special equipment, with the main goal to improve volume stability, strength, permeability and durability of the soil. The development of better strengths than the initial ones is possible due to the reduction of the initial void volume, by replacing the fluid in the structure of the soil with the stabilizing agent used, so the particles and the aggregates get closer together, increasing the number of contact points and at the same time preventing the swelling.
This soil treatment can be used as a practical, economic and environmental solution for a wide range of engineering applications. Some of the soil-mixing applications are road/rail embankments, lime, cement or lime/cement columns for excavation support, marine clays improvement for offshore platforms, shallow foundations, dam reinforcement, slope stability amelioration, silos foundations and reduction of seismic pile displacement
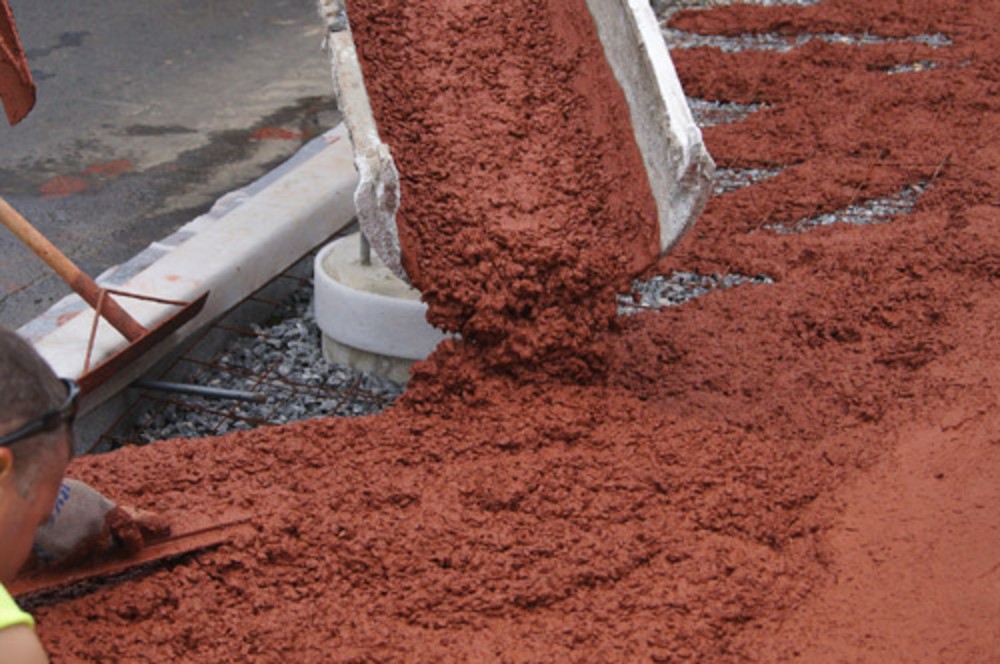
The most used materials for this technology are cement and lime, but there are many other materials that can be used as stabilizing agents. The most used materials used in the stabilization by unique binder or mixed with other binders include: volcanic ash, bentonite, silica fume, bitumen, grinded furnace slag etc. These stabilizers are added either in dry form or in the form of a slurry in different proportions, these specifications being based on the study of the behavior of the mechanical parameters and of various complex mixtures by means of laboratory tests.